Supervise and audit your IT park #CyberSecMonth
Ensure the security of the information system
Implementing solely the measures we have previously recommended is not enough to guarantee the security of your IT park. Indeed, it is important to use control methods to ensure this. In short, you can consider implementing the following :
- Monitor security
- Control Audits
- In-house training
- Collaboration with qualified external service providers.
These tips will help you to react quickly and securely on your IT park.
What you need to oversee and audit your IT park
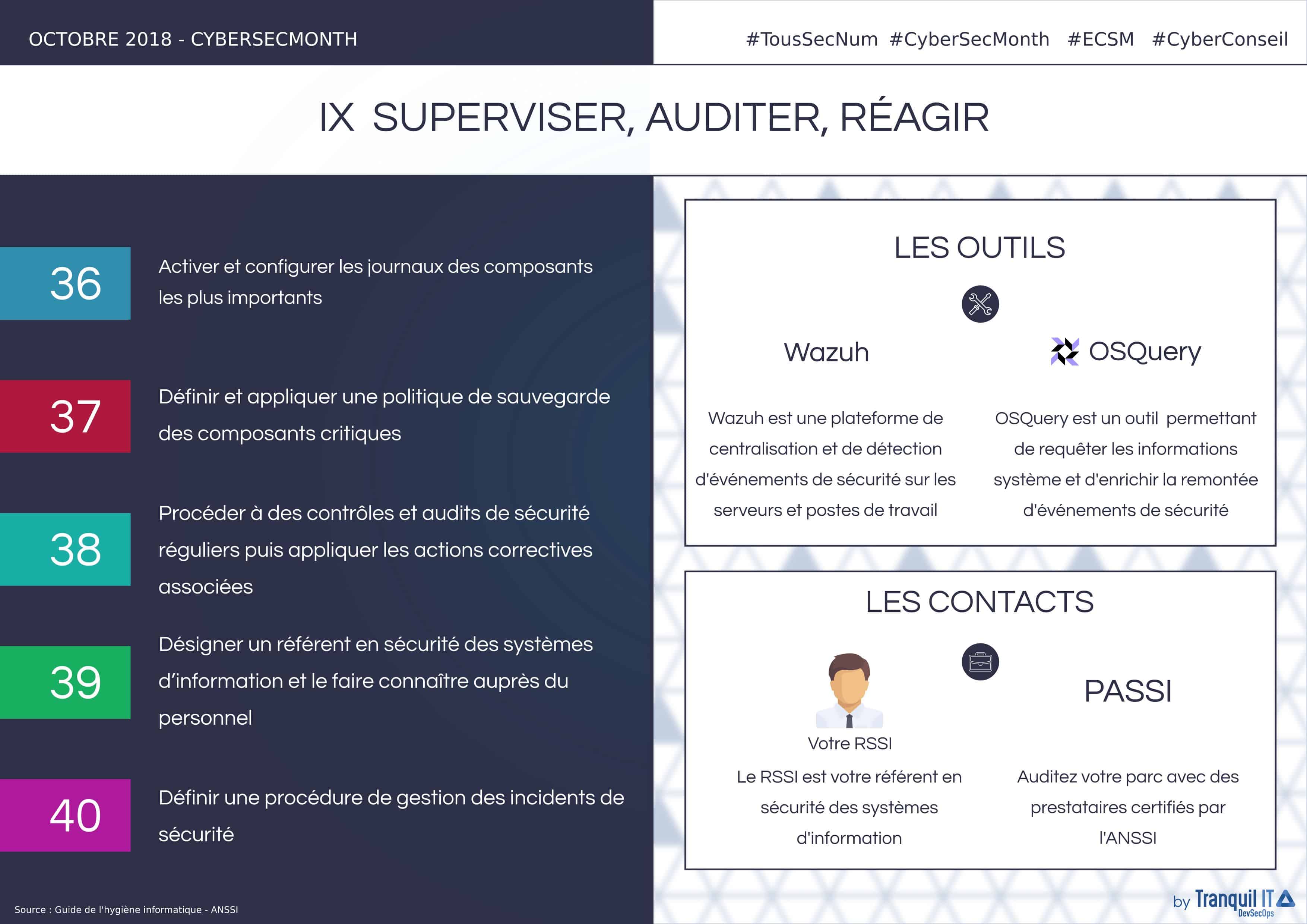
Log the most important components:
The centralization and analysis of relevant logs is more than recommended as it allows the detection of potential malfunctions or illegal access attempts that may affect the integrity of the information system. The implementation of a centralization tool for these logs allows real-time analysis of vital components of the information system such as network and security equipment, servers and user workstations. All these elements must be subject to an analysis of the configuration of the logged elements (format, file rotation frequency, maximum log file size, recorded event categories) to adapt them. Safety-critical events must be logged and kept for at least one year. A contextual study of the system must be carried out and the following elements must be logged:
- Firewall : Blocked packages
- Systems and applications : Authentications and authorizations (failures as well as successes), unexpected stops
- Services : Protocol errors (such as 403, 404, 500 errors for HTTP services), traceability of application flows to interconnections (URL on an HTTP relay, message headers on an SMTP relay, etc)
In order to be able to correlate events between the different components, their time synchronization source (using the NTP protocol) must be identical.
Implement a backup policy for critical components:
It is essential to be able to access backups (stored in a safe place) after an operating incident or an intrusion into the information system. To do this, it is strongly recommended to formalize a regularly updated backup policy so that the organization develops a real requirement for the backup of information, software and systems. This policy must include:
- The list of data considered vital for organization and servers concerned
- The different types of backup (such as offline mode)
- The frequency of backups
- The procedure for administering and executing backups
- Storage information and backup access restrictions
- Restoration test procedures
- The destruction of the media that contained the backups
Restoration tests can be performed in several ways:
- Systematic, by a task scheduler for important applications
- Punctual, in case of error on the files
- General, for a full backup and restoration of the information system
Perform frequent security checks and audits:
It is important to audit the information system at least once a year in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the measures implemented and their maintenance over time. This makes it easier to measure the differences between the rules adopted by the entity and their application. These audits can be carried out by internal audit teams or by specialized external companies. Depending on the scope to be controlled, technical and/or organizational audits will be carried out by the professionals involved. These audits are necessary if the entity must comply with regulations and legal obligations directly related to its activities.
Following these audits, it is necessary to identify corrective actions, plan the application of these corrections and develop follow-up points at regular intervals. It is also recommended to set up indicators on the progress of the action plan (through a comprehensive and organised dashboard). However, the audit should not be the only element of control since it does not systematically guarantee the security of the information system and may omit possible vulnerabilities.
Designate a referent in the information system security:
Organizations must designate a referent in terms of information systems security, who must be supported by management or a specialized decision-making body depending on the maturity level of the entity. This referent should be trained in information systems security and crisis management. Within the organization, he or she must be known to all users and will be the first point of contact for all questions relating to information system security:
- The definition of the rules to be applied according to the context
- Verification of the application of the rules
- Raising user awarness and defining a training plan for IT staff
- Centralization and processing of security incidents observed or reported by users
In the most important entities, this correspondent can be designated to become the relay of the CISSO. For example, they will be responsible for reporting users complaints and identifying the topics to be addressed to raise awareness in order to improve the level of security of the information system within the organization.
Establish a procedure for managing security incidents:
An intrusion can be detected by unusual behavior of a workstation or server (impossible connection; important or unusual activities; unauthorized open services; unauthorized file modification; multiple antivirus alerts). However, a poor response to a security incident can make the situation worse and even prevent its resolution. In the case of an intrusion, it is advisable to:
- Disconnect the machine from the network in order to interupt the attack
- Keep the machine powered up to not to lose any valuable information
- Do not restart the machine
- Inform the hierarchy and the referent in information system security
Thereafter, it is recommended to contact a Security Incident Response Service Provider (SIRP) to perform the necessary technical operations (physical copy of the disk; analysis of memory, logs and possible malicious codes; etc.) and to determine if other elements of the information system have been compromised. It will also involve developing the response to remove any malicious codes and access available to the attacker and changing compromised passwords. Any incident must be recorded in a centralized register. A complaint may also be filed with the competent judicial service.
Audit your fleet, the starting point
It’s complicated for an organization to have the necessary resources to reliably audit their IT assets. The enterprise does not necessarily have the tools or know-how to perform a full internal audit. Using an Information Systems Security Audit Service Provider (PASSI) is therefore recommended to build a real cybersecurity strategy. PASSI audits fall into several categories
- Architecture audit
- Configuration audit
- Source code audit
- Intrusion test
- Organizational and physical audit
ANSSI certifies the audit bodies on each of these criteria individually. Not all PASSI are qualified for all criteria, refer to the PASSI list for more information. Once your audit has been carried out, we can help you to apply the audit body’s recommendations.
Rely on our expertise to supervise and audit your computer equipment
Driven by the desire to help organizations in the management of their IT systems, our objective is to assist system administrators in their daily missions. This goal is the result of more than 15 years of experience in IT asset management and local network security (security barriers, user rights management, application control, workstation updates, etc.). In order to guarantee the security of your fleet, we prefer tools that we have developed (such as WAPT, software deployment solution) or on which we have real expertise (such as Samba Active Directory), while maintaining our DevSecOps philosophy.
Within Tranquil IT, we have always wanted to privilege Open Source tools for their reliability, maintainability but also the freedom they offer. Choosing Open Source means choosing to save on licensing costs and trust our experts!
Do you need to secure your computer equipment?
Cybersecurity: See you in November!
Although cybersecurity is the focus of attention during the month of October, the real objective of CyberSecMonth is to raise awareness of digital security issues among as many people as possible. The purpose of this event is to develop these tips and good reflexes throughout the year and this is why the European Cyber Week will punctuates the news of November! This year, the event takes place in Rennes from 19 to 22 November and focuses on artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.
Articles not to be missed:
- Cyber Scams: Don’t get trapped – AB Consulting
- Credit card fraud: How to protect yourself? – Ministère de l’intérieur
- 10 tips to recognize a phishing email – AB Consulting
- Cyber-risk: Emerging technologies and privacy – AB Consulting
Find all our recommendations on Twitter and LinkedIn and on hashtag : #TousSecNum, #CyberSecMonth, #ECSM2018 and#ECSM. Also follow our hashtag #CyberConseil to follow Tranquil IT’s advice and discover the following graphics.
OpenRSAT — A free, cross-platform alternative to Microsoft’s RSAT
OpenRSAT is a free and open source solution that allows system administrators to manage an Active Directory (AD) environment directly from any operating system: Windows, macOS, and Linux. Designed as a lightweight alternative to Microsoft's RSAT (Remote Server...
Tranquil IT and open source software: a shared history
Founded in 2002 by brothers Vincent and Denis Cardon, Tranquil IT embodies the spirit of innovation and commitment to open source software. Driven by a shared passion for open source, we have evolved from an IT outsourcing business to a solutions development company,...
Tranquil IT and Green IT
In a world where ecological transition has become a priority, the IT sector must also adopt more responsible practices. Tranquil IT and Green ITThe environmental footprint of digital technology is significant, particularly due to the production of hardware and the...










